background and overview[1]
the chinese alias of 1-phenylpyrrolidine is n-phenylpyrrolidine. n-substituted five-membered nitrogen heterocyclic compounds including 1-phenylpyrrolidine are an important basic structural unit in organic compounds and often appear in biologically active natural products and drug molecules. the synthesis of n-substituted five-membered nitrogen heterocyclic compounds has therefore received widespread attention. at present, there are two common ways to synthesize such compounds: 1. under the catalysis of iron, copper, palladium and other metal compounds, it is synthesized from halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons and five-membered nitrogen heterocyclic compounds, for example, from n heterocyclic carbene palladium complex synthesis of n-aryl tetrahydropyrrole catalyzed by (s)-proline and cui -synthesis of n-aryl tetrahydropyrrole catalyzed by al alloy; 2. synthesis of n-substituted tetrahydropyrrole compounds from aromatic amines and 1,4-dihalobutane under alkaline conditions, such as in potassium carbonate aqueous solution n-substituted tetrahydropyrrole compounds were synthesized from 1,4-dibromobutane and aromatic amines. in addition, n-substituted tetrahydropyrrole may also be synthesized from aromatic amines and 1,4-butanediol or tetrahydrofuran, but the reaction generally requires that the reaction be carried out under high temperature and pressure.
preparation [1]
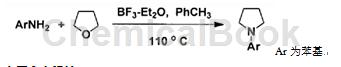
the synthesis of 1-phenylpyrrolidine (1) is as follows: under argon protection, add 0.15ml (1.2mmol, 170.3mg) boron trifluoride ether solution and 0.1ml (1mmol, 93mg) aniline at room temperature. 4 ml of freshly steamed toluene was stirred at room temperature for 60 min, then 1.0 ml (10 mmol) of tetrahydrofuran was added, the temperature was slowly raised to 110°c, and refluxed for 24 h. the reaction system was lowered to room temperature, 10 ml of saturated sodium bicarbonate solution was added, stirred thoroughly, and extracted with dichloromethane (3 × 10 ml). the organic phases were combined and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and 87 mg of the product was obtained as a light yellow oil through silica gel column chromatography using petroleum ether (60-90°c): dichloromethane = 1:4 (volume ratio) as the developing solvent. the yield was 59%. the nuclear magnetic data are as follows: 1h nmr (solvent: cdcl 3 , chemical shift): δ1.96-1.99 (m, 4h), 3.25-3.28 (m, 4h) ), 6.56 (d, j=7.9hz, 2h), 6.64 (t, j=7.3hz, 1h), 7.21 (td, j=6.8, 0.9hz, 2h); 13c nmr (solvent: cdcl 3 , chemical shift): δ25.7, 47.8, 111.9, 115.6, 129.3, 148.2;
main reference materials
[1] cn107935965 a new synthesis method of n-substituted tetrahydropyrrole derivatives


